C. For Loop & While Loop
- Two types of scripts: Sequential vs Iterative
- Iterative scripts = Loop
- For loop (based on counter/list) & While loop (based on condition)
- Do repeated actions

A. File I/O:
open(path[,mode='r']) function..readlines() method will extract all content in the file as a list of strings. One paragraph, one string..write(string) method write the given content to the file, from the beginning of file if mode 'w' is used or from the bottom of file if mode 'a' is used..close() method\n.strip()/ to denote directory# Create a new file named "text.txt" in the current folder
file = open('text.txt','w')
#add three new lines, separated by line break mark \n
file.write("Hello world!\n")
file.write("COMM 7780\n")
file.write("Bye bye!\n")
9
#close it
file.close()
# Create a child folder test
# Create another file named "text2.txt" in the child folder
file2 = open("./test/text2.txt", "w")
file2.close()
# Create a file named "text3.txt" on Desktop
file3 = open("C:/Users/yuner/Desktop/text3.txt",'w')
file3.close()
#Read text.txt file
file = open('text.txt','r')
#read the existing lines into a list
lines=file.readlines()
#print out the first line
lines[0]
'Hello world!\n'
B. If/Else Statement
if logical_condition1 :... (else: ...)if a==1: print('yes') #Block A else: print('no') #Block B``` >
x = 1
if x==0:
print('ZERO!')
print('Yes!')
else:
print('Not Zero!')
print('No!')
print('Done!')
Not Zero! No! Done!
x = 2
if x==0:
print('ZERO!')
print('Yes!')
elif x==1:
print('ONE!')
print('No!')
else:
print("Not ZERO nor ONE!")
print('Done!')
Not ZERO nor ONE! Done!
Write a program to determine if a number x is positive.
If x is positive, determine if it is odd or even.
C. For Loop & While Loop

while loop is used to repeatedly execute a block of commands while a condition is True.while condition: #loop condition statements #loop body
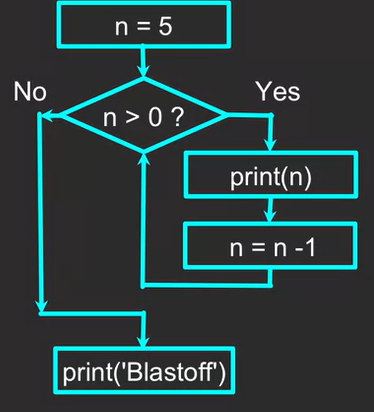
statements refer to a block of commands subordinate to while loop. They are only functional within for loop. Python requires INDENT Tab or 4 spaces to group commands into block. For example:n=5 while n>0: print(n) #Use indentation to denote a Block subordinate to while loop n-=1 #Decrease by 1 unit print('Blastoff!') #Out of the while loop
Write a GUESS NUMBER program using while loop:
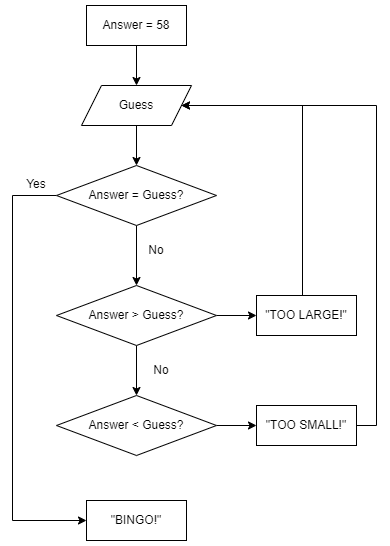
#Write your codes here
answer = 58
for loop is used to step through items in a list and repeatedly execute a block of commands for each item.for var in object_list: #Assign object items to target statements #Loop body
- `for` loop naturally includes a step for variable assignment: assign every value in the list to variable var
- Usually coupled with `range([start=0,] stop[, step=1])` function, which will automatically create a list of whole numbers ranging from the start number and stopping at but <font color="red">not including the stop number</font>.
- range(5) = [0,1,2,3,4]
- range(1,5) = [1,2,3,4]
- range(0,5,2) = [0,2,4], Step = 2
- Syntax: Indentation within the for loop:
>```python
for a in range(5):
print(a) #Use indentation to denote loop body
print(a+1)
print(a+2)
#Use for loop to print out the first 10 whole numbers
#Use for loop to print out all EVEN numbers smaller than 25
#Use for loop to print out the sum of the first 100 whole numbers
#Read lines in text.txt and print out the number of CHARACTERS, including spaces, and the number of WORDS in each line
#Repeat every line three times, i.e. copy each line and paste it three times to the file.
#Save the outputs.
#Cut lines in above created file by words. One word, one line. Save the outputs.
a=[0,1,2,3]
#two ways to increase every element in a by one unit
#---------------------------------
#1
b=[]
for i in a:
b.extend([i+1])
print(b)
#2
b=[i+1 for i in a]
print(b)
#Try continue statement
for i in range(10):
if 2<i<5:
continue
print(i)
#Try break
for i in range(10):
print(i)
if i>5:
break
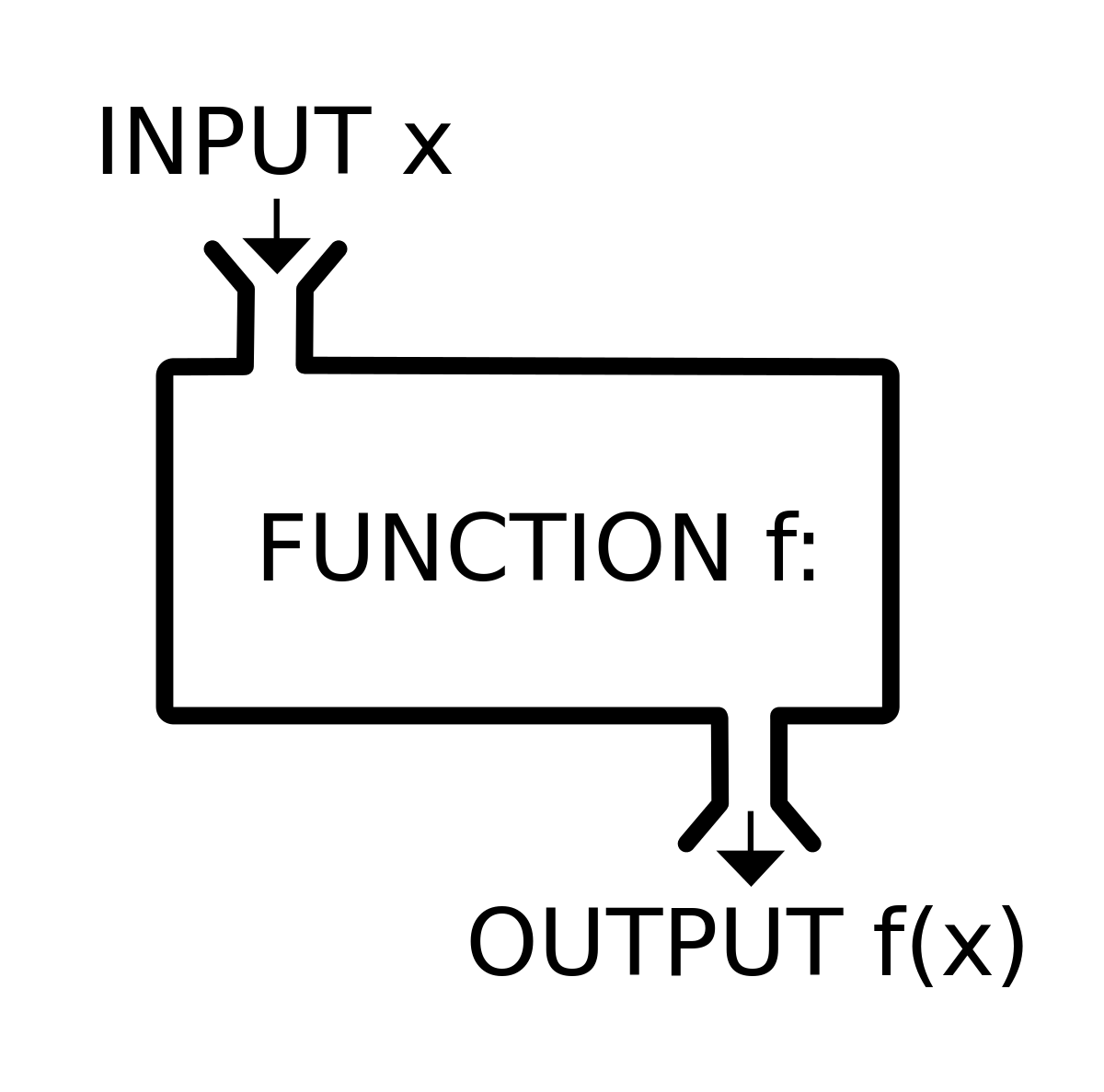
def function_name(input1[,input2,input3...]): command line return ```
#Create a custom function series_sum() to report the sum of the first N whole numbers
#HINT: Input value: n, Output value: sum of the series
def series_sum()
def minus_one(a):
a=a-1
print('local variable a:',a)
return
a=4
print('global variable a:',a)
test(a)
 Presidential inauguration speeches capture the sentiment of the time.
Presidential inauguration speeches capture the sentiment of the time.
Download the dataset from:https://juniorworld.github.io/python-workshop//doc/presidents.rar
Expected Objectives:
CLI = 0.0588 * L - 0.296 * S - 15.8
L is the average number of letters per 100 words and S is the average number of sentences per 100 words.
CLI is equivalent to the number of years of education completed by the speaker.
presidents=['Washington','Jefferson','Lincoln','Roosevelt','Kennedy','Nixon','Reagan','Bush','Clinton','W Bush','Obama','Trump']
for president in presidents:
def readablity_test(paragraphs):
#Define a customer function readablity_test() to output sentence_count,word_count and letter_count
#Save results to a csv file